NestJS로 API 만들기
June 18, 2023
0. Introduction
- nest js 는 구조가 있다. 구조 덕분에 순서와 룰이 있어서, 이를 따르기만 하면 큰 규모의 백엔드를 쉽게 만들 수 있다.
- nestJs는 nodeJs의 프레임워크로서, Express 위에서 동작한다.
Insomnia
Insomnia는 개발자 친화적인 인터페이스, 내장된 자동화 및 확장 가능한 플러그인 생태계를 제공하는 Rest 클라이언트이다. 이를 통해 API 엔드포인트를 테스트할 수 있다.
설치
Nest CLI를 사용하면 새 프로젝트를 설정하는 것이 매우 간단하다.
npm이 설치된 상태에서 OS 터미널에서 다음 명령을 사용하여 새 Nest 프로젝트를 만들 수 있다.
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
nest new project-name1. NestJs 구조
module
// app.module.ts
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common"
import { AppController } from "./app.controller"
import { AppService } from "./app.service"
@Module({
imports: [],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}@Module 로 시작하는 코드는 데코레이터이다. 데코레이터는 클래스에 함수 기능을 추가할 수 있다. Modules 모듈은 @Module 데코레이터로 주석이 달린 클래스이다. 데코레이터는 Nest가 애플레이케이션 구조를 구성하는 데 사용하는 메타데이터를 제공한다.
모듈은 Nest에서 애플리케이션 구조를 범위로 구성하는 데 사용된다. 컨트롤러와 공급자는 선언된 모듈에 따라 범위가 지정된다. 모듈과 해당 클래스는 Nest가 DI(종속성 주입)를 수행하는 방법을 결정하는 그래프를 형성한다.
https://docs.nestjs.com/modules#modules
controllers
NestJs는 main.ts 파일에서 시작하며, 해당 파일 안에서 하나의 AppModule을 생성한다. AppModule은 모든 것의 루트 모듈과 같다.
컨트롤러는 들어오는 요청을 처리하고(url을 가져오고) 클라이언트에 응답을 반환(함수 실행)하는 역할을 한다. 아래 코드에서 @Get(”/hello”)이 express의 app.get(“/hello”, getHello)처럼 라우터 같은 역할을 한다.
// app.controller.ts
import { Controller, Get } from "@nestjs/common"
import { AppService } from "./app.service"
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly appService: AppService) {}
@Get("/hello")
getHello(): string {
return this.appService.getHello()
}
}데코레이터는 꾸미는 함수와 붙어 있어야 한다.
@GET은 GET 요청이고, @POST는 POST 요청을 한다.
https://docs.nestjs.com/controllers
services
NestJS는 컨트롤러에서 비즈니스 로직을 분리하고 싶어한다. 컨트롤러의 책임은 들어오는 url 요청을 처리하여 응답을 반환하는 것이다. 나머지 비즈니스 로직은 서비스로 분리된다.
// app.service.ts
import { Injectable } from "@nestjs/common"
@Injectable()
export class AppService {
getHello(): string {
return "Hello World!"
}
}2. Rest API
- nest 가능한 명령어 확인
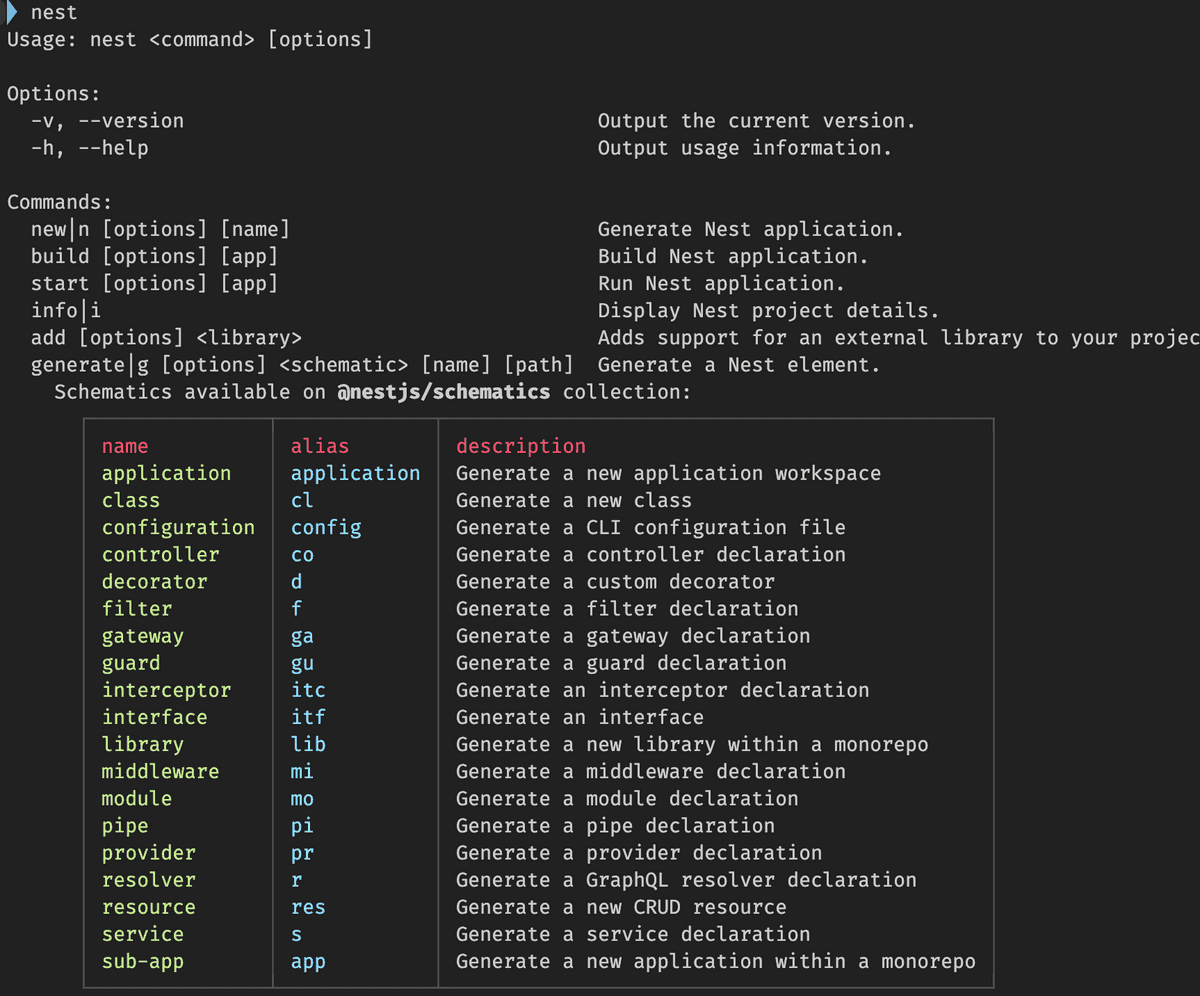
nest g co // 컨트롤러 생성위와 같은 컨트롤러 생성 명령어 실행 시, 컨트롤러가 생성되고 모듈에 컨트롤러가 자동으로 주입된다.
Param
Param은 Path Variable을 받아올 때 사용하며 요청 주소에 포함되어있는 변수를 담는다. (예, /users/123에서 123) 만약 어떤 resource를 식별하고 싶으면 Path Variable을 사용한다.
import { Controller, Get, Param, Post, Delete, Patch } from "@nestjs/common"
@Controller("movies")
export class MoviesController {
@Get()
getAll() {
return "This will return all movies"
}
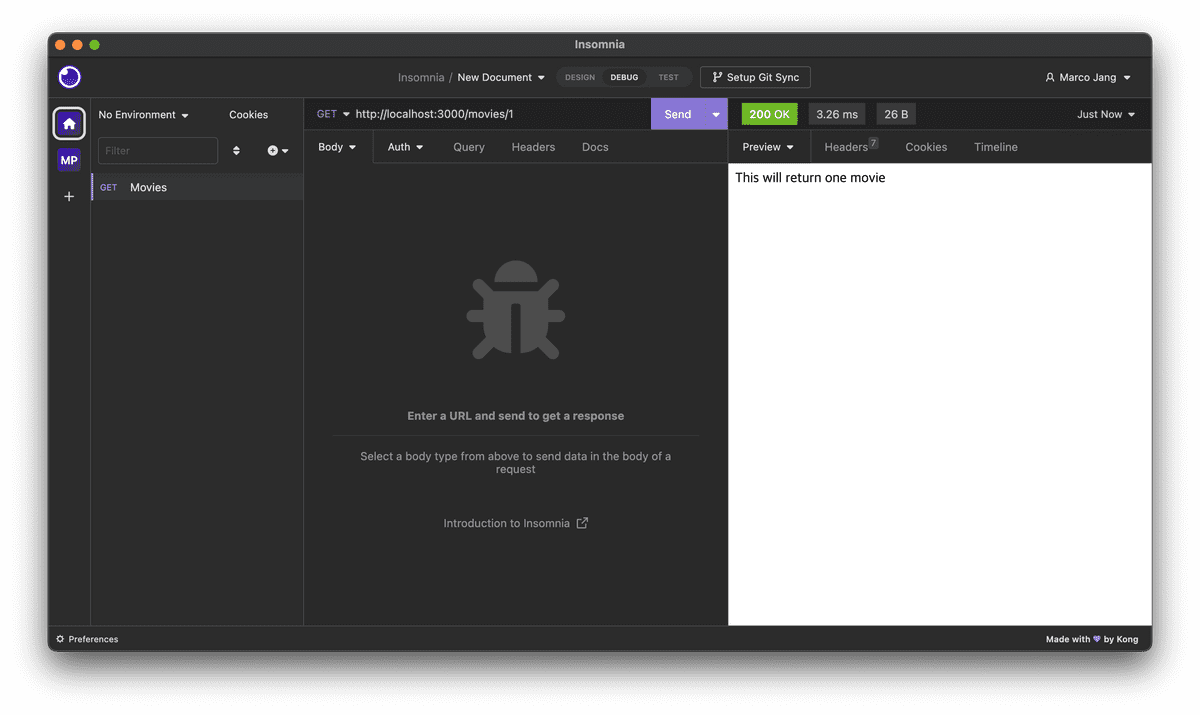
@Get("/:id")
getOne(@Param("id") movieId: string) {
return `This will return one movie with the id:${movieId}`
}
@Post()
create() {
return "This will create a movie"
}
@Delete("/:id")
remove(@Param("id") movieId: string) {
return `This will delete a movie with the id:${movieId}`
}
@Patch("/:id")
patch(@Param("id") movieId: string) {
return `This will patch a movie with the id:${movieId}`
}
}insomnia에서 api 테스트할 수 있다.
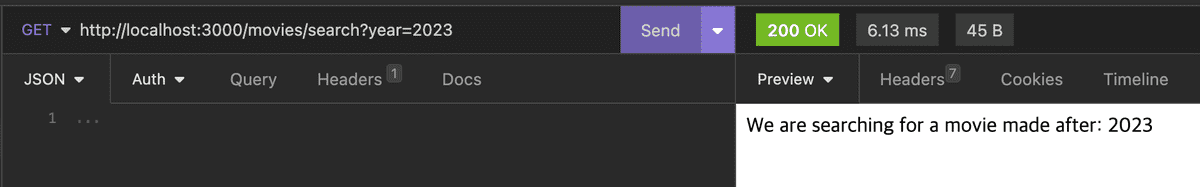
Query
Query는 Query Parameter를 받아올 때 사용하고, 주소 이후에 ”?” 뒤에 있는 변수를 담는다. (예, /users?id=123 에서 id=123)
정렬이나 필터링을 한다면 Query Parameter를 사용하는 것이 적절하다.
@Get('search')
search(@Query('year') searchingYear: string) {
return `We are searching for a movie made after: ${searchingYear}`;
}
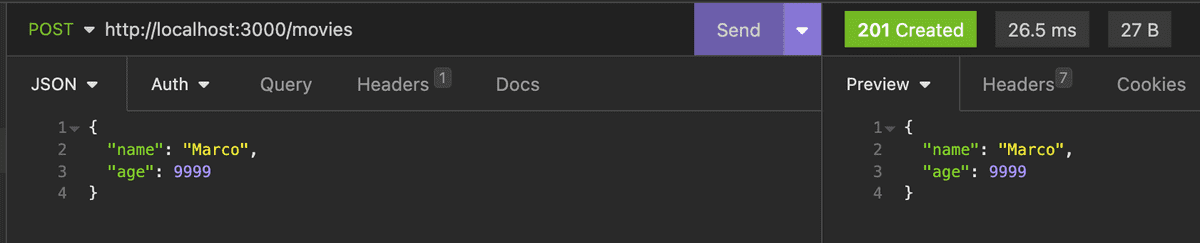
Body
@Post()
create(@Body() movieData) {
return movieData;
}
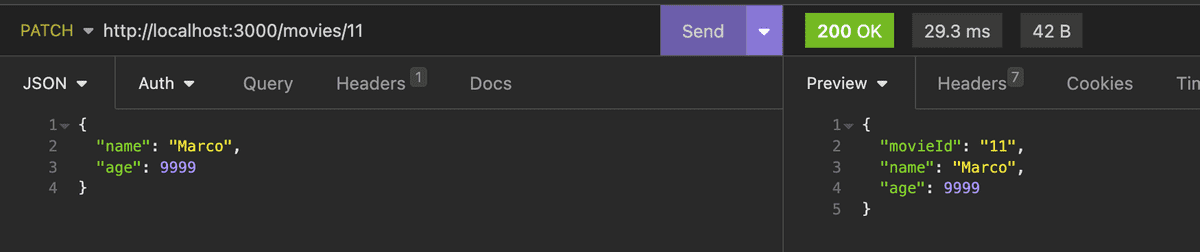
@Patch('/:id')
patch(@Param('id') movieId: string, @Body() updateData) {
return { movieId, ...updateData };
}
services
nest g sentites에 실제로 데이터베이스 모델을 만들어야 한다.
- 인터페이스는 컴파일 후 자바스크립트 코드로 남지 않는다. 반면, 클래스는 서버에서 컴파일 후 자바스크립트 코드로 남아 있으므로 사용할 수 있다.
// entities/movie.entity.ts
export class Movie {
id: number
title: string
year: number
genres: string[]
}SRP에 따라 서비스에 비즈니스 로직을 짠다. 아래는 가짜 데이터베이스 유사 코드이다.
// movies.service.ts'
import { Injectable, NotFoundException } from "@nestjs/common"
import { Movie } from "./entities/movie.entity"
@Injectable()
export class MoviesService {
private movies: Movie[] = []
getAll(): Movie[] {
return this.movies
}
getOne(id: string): Movie {
const movie = this.movies.find(movie => movie.id === +id)
if (!movie) {
throw new NotFoundException(`Movie with ID ${id} not found.`)
}
return movie
}
deleteOne(id: string) {
this.getOne(id)
this.movies = this.movies.filter(movie => movie.id !== +id)
}
create(movieData) {
this.movies.push({
id: this.movies.length + 1,
...movieData,
})
}
update(id: string, updateData) {
const movie = this.getOne(id)
this.deleteOne(id)
this.movies.push({ ...movie, ...updateData })
}
}-
Built-in HTTP exceptions
- 위 코드에서 NotFoundException 같은 예외는 Nest가 제공하는 기본 HttpException에서 상속되는 일련의 표준 예외 중 하나이다. 이러한 표준 예외들은 @nestjs/common 패키지에서 가져올 수 있으며 일반적인 HTTP 예외를 나타낸다.
- https://docs.nestjs.com/exception-filters#built-in-http-exceptions
// movies.controller.ts
import {
Controller,
Get,
Param,
Post,
Delete,
Patch,
Body,
Query,
} from "@nestjs/common"
import { MoviesService } from "./movies.service"
import { Movie } from "./entities/movie.entity"
@Controller("movies")
export class MoviesController {
constructor(private readonly moviesService: MoviesService) {}
@Get()
getAll(): Movie[] {
return this.moviesService.getAll()
}
@Get("/:id")
getOne(@Param("id") movieId: string): Movie {
return this.moviesService.getOne(movieId)
}
@Post()
create(@Body() movieData) {
return this.moviesService.create(movieData)
}
@Delete("/:id")
remove(@Param("id") movieId: string) {
return this.moviesService.deleteOne(movieId)
}
@Patch("/:id")
patch(@Param("id") movieId: string, @Body() updateData) {
return this.moviesService.update(movieId, updateData)
}
}DTO - class-transformer, class-valiadator
DTO(Data Transfer Object, 데이터 전송 객체) 타입을 통해 코드를 간결하게 만드는 데 도움을 주고, NestJS가 들어오는 쿼리에 대해 유효성을 검증할 수 있게 해준다.
DTO를 만들고 유효성 검사를 할 데코레이터를 추가한다.
npm i class-transformer class-validatorhttps://github.com/typestack/class-validator#usage
// movie/dto/create-movie-dto.ts
import { IsString, IsNumber } from "class-validator"
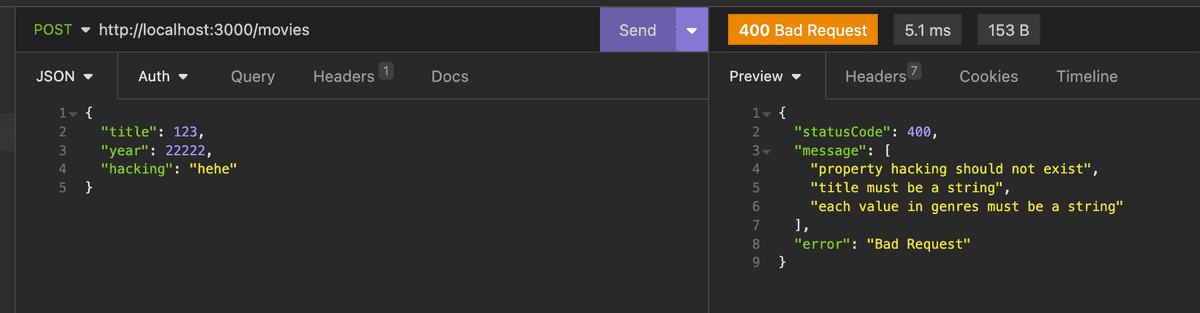
export class CreateMovieDto {
@IsString()
readonly title: string
@IsNumber()
readonly year: number
@IsString({ each: true })
readonly genres: string[]
}들어오는 쿼리에 대해 유효성을 검증할 코드를 파이프라고 칭할 수 있으며 일종의 미들웨어와 유사하게 생각할 수 있다. 파이프를 만들어보자. app.useGlobalPipes 는 main.ts에 추가해야 한다.
- whitelist: true로 설정하면 유효성 검사기는 class-validator의 유효성 검사 데코레이터를 적어도 하나라도 사용하지 않은 모든 속성 객체를 제거합니다.
- forbidNonWhitelisted: true로 설정했을 때, DTO에 데코레이터가 없는 속성은 HttpException 을 던진다. forbidNonWhitelisted 옵션은 whitelist에서 유효한 속성이 아닌 것을 제외하는 것 대신에 에러를 날려주는 것이기 때문에, 먼저 whitelist 옵션이 true로 되어있어야 사용 가능한 옵션이다.
- transform: true로 설정하면 ValidationPipe는 payload를 DTO 클래스에 따라 유형이 지정된 객체로 자동 변환한다.
// main.ts
import { NestFactory } from "@nestjs/core"
import { AppModule } from "./app.module"
import { ValidationPipe } from "@nestjs/common"
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule)
app.useGlobalPipes(
new ValidationPipe({
whitelist: true,
forbidNonWhitelisted: true,
transform: true,
})
)
await app.listen(3000)
}
bootstrap()
- class-validator의 @IsOptional() 은 값이 empty(또는 null또는 undefined)여도 유효성검사를 무시한다.
DTO - mapped-types
mapped-types는 DTO 타입을 변환시키고 사용할 수 있게 해주는 패키지이다.
https://docs.nestjs.com/openapi/mapped-types
@nestjs/swaggerimport { ApiProperty } from "@nestjs/swagger"
export class CreateCatDto {
@ApiProperty()
name: string
@ApiProperty()
age: number
@ApiProperty()
breed: string
}PartialType()부모 DTO의 모든 속성들을 물려받지만 전부 Optional
export class UpdateCatDto extends PartialType(CreateCatDto) {}PickType()부모 DTO의 속성 중 몇 개만 골라서 물려받음
export class UpdateCatAgeDto extends PickType(CreateCatDto, ["age"] as const) {}OmitType()부모 DTO의 속성 중 몇 개를 제외하고 물려받음.
export class UpdateCatDto extends OmitType(CreateCatDto, ["name"] as const) {}IntersectionType()은 여러 부모 DTO의 속성들을 모두 물려받음.
export class AdditionalCatInfo {
@ApiProperty()
color: string
}export class UpdateCatDto extends IntersectionType(
CreateCatDto,
AdditionalCatInfo
) {}composition: 위와 같은 타입 매핑 유틸리티 함수는 합성 가능하다.
export class UpdateCatDto extends PartialType(
OmitType(CreateCatDto, ["name"] as const)
) {}Modules and Dependency Injection
movies module을 새로 만들고, app module로부터 movies module을 분리할 수 있다.
// 모듈 만들기
nest g mo// app.module.ts
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common"
import { MoviesModule } from "./movies/movies.module"
@Module({
imports: [MoviesModule],
controllers: [],
providers: [],
})
export class AppModule {}// movies.module.ts
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common"
import { MoviesController } from "./movies.controller"
import { MoviesService } from "./movies.service"
@Module({
controllers: [MoviesController],
providers: [MoviesService],
})
export class MoviesModule {}Express on NestJS
NestJS는 Express 프레임워크 위에서 돌아간다. 그러나 Fastify 라이브러리 위에서 돌아가도록 전환할 수 있다. Fastify는 성능 향상 장점이 있다.
Express 프레임워크 위에서 돌아가므로 @req, @res 객체를 사용할 수 있으나, Fastify 로 전환하는 경우 호환되지 않는 문제가 발생하므로 Express에서만 돌아가는 객체를 많이 사용하지 않는 것이 바람직하다.
3. Unit Test
유닛 테스트는 시스템에서 함수 같은 하나의 유닛만을 각각 테스트하는 방법이다. 반면, e2e 테스트는 전체 시스템을 테스트하는 방법이다.
Test setup - MoviesService 정의
import { Test, TestingModule } from '@nestjs/testing';
import { MoviesService } from './movies.service';
import { NotFoundException } from '@nestjs/common';
describe('MoviesService', () => {
let service: MoviesService;
beforeEach(async () => {
const module: TestingModule = await Test.createTestingModule({
providers: [MoviesService],
}).compile();
service = module.get<MoviesService>(MoviesService);
});
it('should be defined', () => {
expect(service).toBeDefined();
});getAll, getOne 테스트
describe("getAll", () => {
it("should return an array", () => {
const result = service.getAll()
expect(result).toBeInstanceOf(Array)
})
})
describe("getOne", () => {
it("should return a movie", () => {
service.create({
title: "Test Movie",
genres: ["test"],
year: 2000,
})
const movie = service.getOne(1)
expect(movie).toBeDefined()
})
it("should throw 404 error", () => {
try {
service.getOne(999)
} catch (e) {
expect(e).toBeInstanceOf(NotFoundException)
}
})
})delete, create 테스트
describe("deleteOne", () => {
it("deletes a movie", () => {
service.create({
title: "Test Movie",
genres: ["test"],
year: 2000,
})
const beforeDelete = service.getAll().length
service.deleteOne(1)
const afterDelete = service.getAll().length
expect(afterDelete).toBeLessThan(beforeDelete)
})
it("should return a 404", () => {
try {
service.deleteOne(999)
} catch (e) {
expect(e).toBeInstanceOf(NotFoundException)
}
})
})
describe("create", () => {
it("should create a movie", () => {
const beforeCreate = service.getAll().length
service.create({
title: "Test Movie",
genres: ["test"],
year: 2000,
})
const afterCreate = service.getAll().length
expect(afterCreate).toBeGreaterThan(beforeCreate)
})
})4. E2E Test
import { Test, TestingModule } from "@nestjs/testing"
import { INestApplication, ValidationPipe } from "@nestjs/common"
import * as request from "supertest"
import { AppModule } from "./../src/app.module"
describe("AppController (e2e)", () => {
let app: INestApplication
beforeAll(async () => {
const moduleFixture: TestingModule = await Test.createTestingModule({
imports: [AppModule],
}).compile()
app = moduleFixture.createNestApplication()
app.useGlobalPipes(
new ValidationPipe({
whitelist: true,
forbidNonWhitelisted: true,
transform: true,
})
)
await app.init()
})
describe("/movies", () => {
it("GET", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.get("/movies")
.expect(200)
.expect([])
})
it("POST 201", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.post("/movies")
.send({
title: "Test",
year: 2000,
genres: ["test"],
})
.expect(201)
})
it("POST 400", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.post("/movies")
.send({
title: "Test",
year: 2000,
genres: ["test"],
other: "thing",
})
.expect(400)
})
it("DELETE", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.delete("/movies")
.expect(404)
})
})
describe("/movies/:id", () => {
it("GET 200", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.get("/movies/1")
.expect(200)
})
it("GET 404", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.get("/movies/999")
.expect(404)
})
it("PATCH 200", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.patch("/movies/1")
.send({ title: "Updated Test" })
.expect(200)
})
it("DELETE 200", () => {
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.delete("/movies/1")
.expect(200)
})
})
})-
테스트에서도 실제 어플리케이션의 환경을 적용해줘야 한다. 아래와 같은 pipe 적용이 기존 테스트 설정에서 생략되어 있었는데 실제 어플리케이션 환경과 동일하게 하기 위해 추가한다.
app.useGlobalPipes( new ValidationPipe({ whitelist: true, forbidNonWhitelisted: true, transform: true, }) ) -
beforeEach(fn, timeout)
- 각각의 테스트가 실행되기 전에 매번 함수를 실행한다.
- 각각의 테스트 전에 각 테스트에서 사용할 전역 상태를 재설정하려는 경우에 유용하다.
- 함수가 promise을 반환하거나 generator인 경우 Jest는 테스트를 실행하기 전에 해당 promise가 해결될 때까지 기다린다.
- 밀리초로 대기할 시간을 지정할 수 있다. (기본 시간 5초)
- https://jestjs.io/docs/api#beforeeachfn-timeout
-
beforeAll(fn, timeout)
- 모든 테스트가 실행되기 전에 딱 한 번 함수를 실행한다.
-
afterEach(fn, timeout)
- 각각의 테스트가 완료된 후 함수를 실행한다.
-
afterAll(fn, timeout)
- 모든 테스트가 완료된 후 함수를 실행한다.